
What are Copper Clad Laminates?
CCL or Copper Clad Laminate is the fundamental building block of a printed circuit board. PCB fabricators use copper clad laminates to build several types of boards, most notably, single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layered boards. Laminate Manufacturers use various types of materials to build copper clad laminates, and classify them according to material, characteristics, and performance. Depending on the application, characteristics of the copper clad laminate must change, and must conform to several standards.
Constituents of Copper Clad Laminates
A copper clad laminate has two basic constituents:
- A Core or Substrate
- Copper Foils
The core or substrate is a thin board with flat surfaces that gives the printed circuit board its necessary functionality such as:
- Mechanical Strength or Rigidity
- Electrical Insulation
- Thermal Conductivity
Then copper foils bond with the core on one/two sides to form the copper clad laminate.
Copper foils on the core provide additional electrical functionalities to the printed circuit board such as:
- Electrically Conducting Traces
- Pads for Mounting Components
- Electrically Conducting Plated Through Holes
- Power or Ground Planes
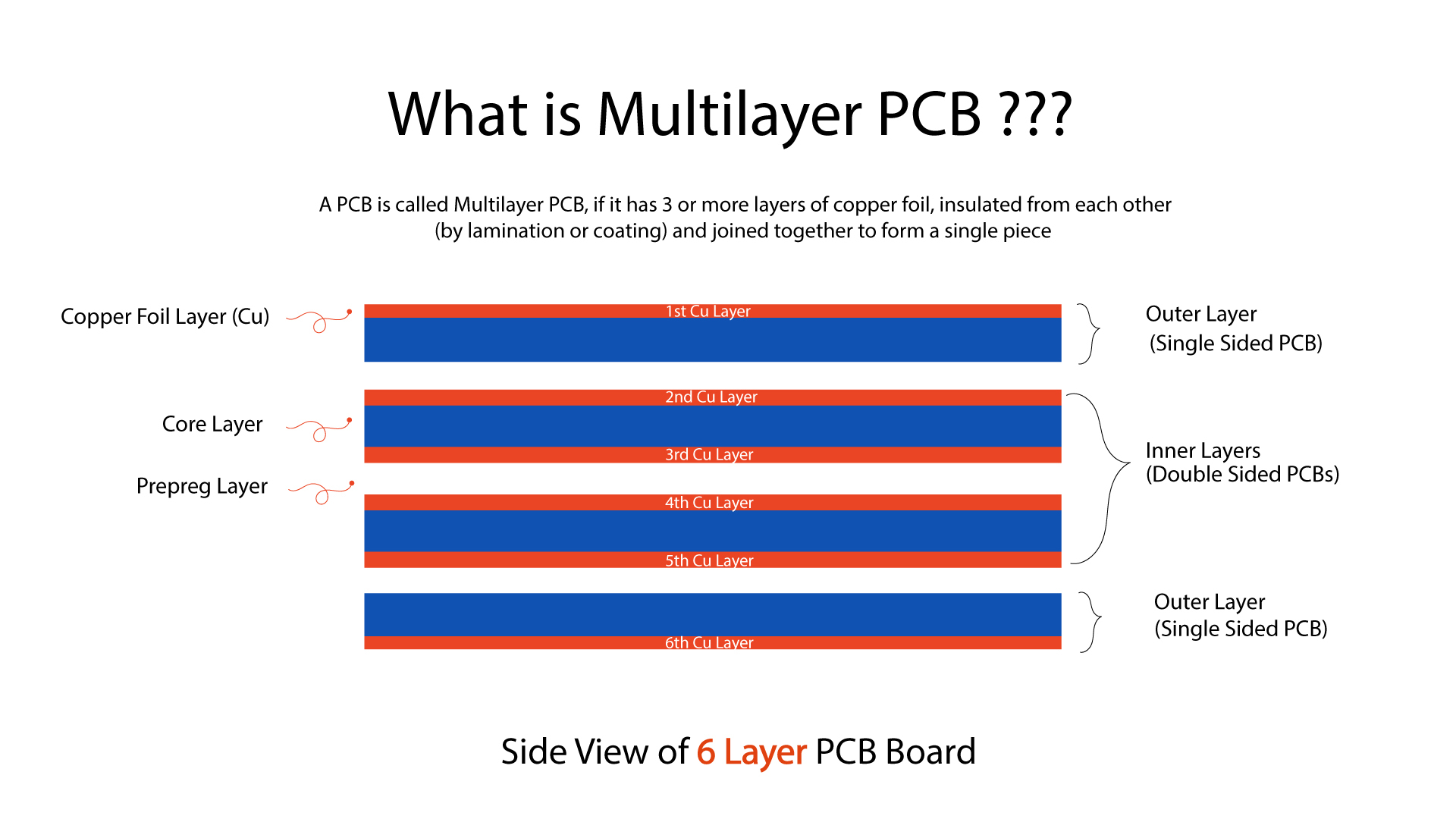
Types of Copper Clad Laminates
Circuit board manufacturing provides each printed circuit board with its own characteristics. This depends on the application of the PCB, which defines its requirements and specifications. During designing of the printed circuit board, engineers must consider the properties of the copper clad laminate making up the specific board. In broad terms, there are primarily two types of copper clad laminates for building PCBs, classified by their mechanical rigidity:
- Rigid Copper Clad Laminates
- Flexible Copper Clad Laminates
Apart from the above, classification of copper clad laminates also depends on their performance in various applications, such as:
- General Performance
- High Heat Resistant Types
- Low Dielectric Constant Types
- Low CTE or Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Types
Rigid Copper Clad Laminate
Fabricators use various insulation materials molded in organic resins for making these copper clad laminates. The cured resin makes the core rigid, hence the name. Although the copper foils are common, the reinforcing insulation material can be:
- Paper Phenolic
- Glass Fiber Cloth
- Metal Core
- Composite Base
- Ceramic Base
Fabricators also use various types of resins for making these copper clad laminates. Among the most popular, these resins include:
- Polyester
- Epoxy
- Cyanate Ester
Flexible Copper Clad Laminates
Applications that need the printed circuit board to bend or flex require the core to be more flexible. To gain flexibility, fabricators make the core of different material, including:
- Polyimide
- Thin Glass Fiber Cloth
- Polyester
Copper Foil
Manufacturers bond copper foils on one or both sides of the core material. This is usually cathodic electrolytic copper that they deposit as a thin continuous layer like a foil on the base insulating core. This type of copper foil has low flexibility and does not promote good signal integrity.
For flexible copper clad laminates, where the thickness of the board is very low, manufacturers use RA or rolled and annealed copper. This type of copper can be very thin, but with high tensile strength, allowing it to flex without suffering cracks due to fatigue.
Pre-Preg Layers
Manufacturers use pre-pregs or a layer of pre-impregnated insulation for separating additional copper layers when making multi-layered printed circuit boards. This is mostly a thin layer of glass fiber cloth impregnated with resin. Usually, the manufacturer pre-dries the resin without curing it, and adds an adhesive layer for strength. This allows the resin to melt, flow, and bond with copper when the fabricator adds more layers.
The pre-preg layers are available in different thicknesses and types. Based on the amount of resin, different versions available are:
- SR or Standard Resin
- MR or Medium Resin
- HR or High Resin
The amount and type of resin depends on the final thickness of the board, its layer structure, and the desired impedance.
Characteristics of Copper Clad Laminates
As copper clad laminates are the basic building block of a printed circuit board, to a large extent, the quality of the board depends on the characteristics of the laminate. Again, depending on the application for a specific PCB, the characteristics of the laminate may have to meet different requirements. That means, all copper clad laminates are not suitable for all types of applications. However, copper clad laminates must meet certain basic requirements irrespective of the applications. These include:
Dimensional Stability :
This technology primarily involves mounting THCs on PCBs. The process starts with the preparation of a program for the auto-inserter machine. Based on the inputs, the auto-inserter arranges THCs in a reel. The inputs necessary are the component sequence, their position, orientation, and span.
Appearance :
Handling the board during manufacturing can lead to dents and scratches. Manufacturing defects such as wrinkles, pinholes, bubbles, resin points, and dents on the copper surface can lead to a wide range of possible issues. This can ultimately result in a poor performance of the copper clad laminate by reflecting on the performance of the printed board.
Electrical Performance :
The electrical performance of the copper clad laminate is of utmost importance, especially for boards meant for high-speed electronic circuits. The electrical performance of the board involves various parameters, including dielectric constant (Dk), dielectric loss tangent (Df), insulation resistance, surface resistance, volume resistance, arc resistance, CTI or comparative tracking index, and electric strength. The designer must carefully consider the above for superior performance.
Environmental Characteristics :
The copper clad laminate must meet specified standards of corrosion resistance and water absorption, to avoid serious performance issues in the field.
Chemicals Characteristics :
The chemical characteristics of the copper clad laminate are also very important parameters, and must meet standard specifications. These include resistance to chemical reagents, Tg or glass transition temperature, dimensional stability, and Z-CTE or Z-axis coefficient of thermal expansion.
Physical Characteristics :
Printed circuit boards pass through several stressful environments during their lifetime, and they must continue to perform with failure. This requires them to confirm to several physical characteristics as per standards. These include resistance to thermal stress (Td, T260, T288, and T300), bending strength, dimensional stability, peel strength, and punching quality.Special Copper Clad Laminates
Different applications are leading to the use of newer and more innovative types of copper clad laminates for meeting more stringent requirements of heat resistance and reliability. Most popular among these special copper clad laminates are:
- Halogen-Free Copper Clad Laminates
- Lead-Free Copper Clad Laminates
Halogen-free Copper Clad Laminates
This category of copper clad laminates come with a specified low content of bromine and chlorine. Halogen-free copper clad laminates have better heat performance, higher thermal decomposition temperatures, and better size stability.
Lead-Free Copper Clad Laminates
This category of copper clad laminates has a surface finish that does not contain Lead or other hazardous substances, conforming to requirements of RoHS and WEEE. Manufacturer use the PN curing system for lead-free copper clad laminates, leading to very good peel strength and bending strength.
Conclusion
The importance of copper clad laminates in printed circuit board manufacturing is immense, considering that the laminate forms the basic building block of a PCB. The copper clad laminate literally gives shape to the board, specifies its characteristics, and defines its performance.



